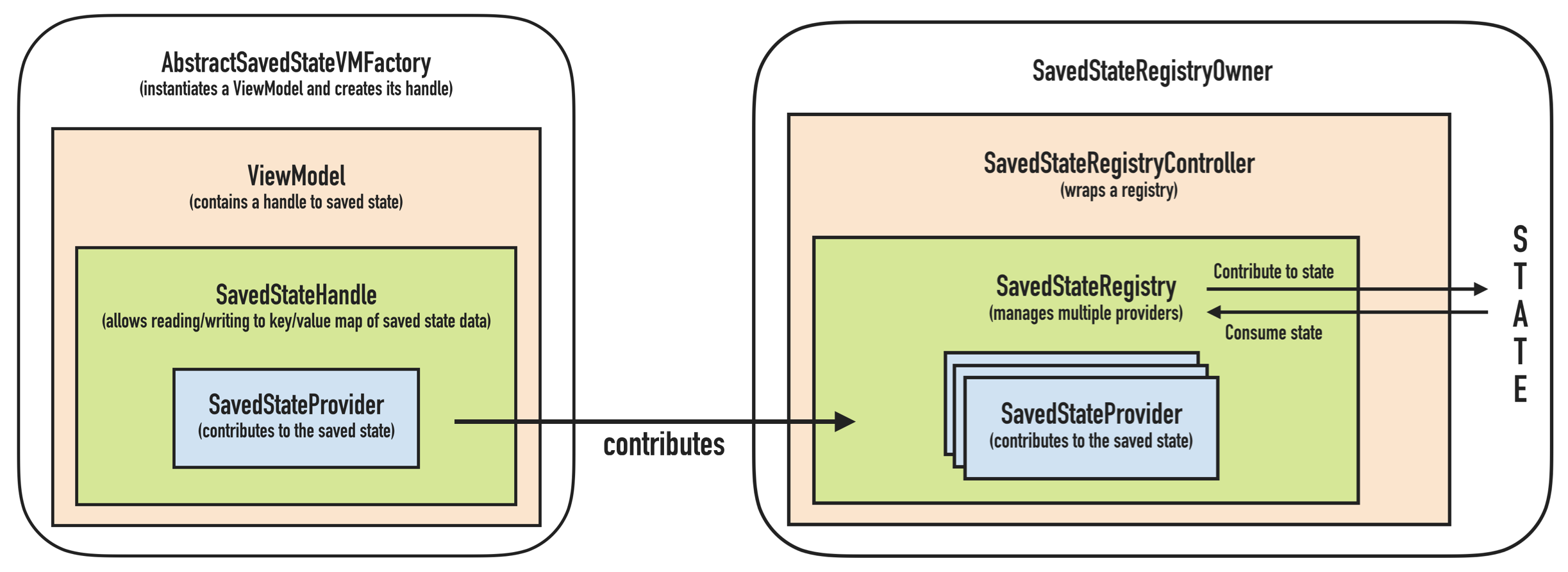
在Android中,如果需要序列化对象可以选择实现 Serializable 或 Parceable。如果是在使用内存的情况下,Parcelable 的效率比 Serializable 高。但 Parcelable 不能被持久化存储,此时还是需要实现 Serializable。
Java实现
首先我们看一个普通的 JavaBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public class PostEntity {
private String name;
private String category;
private String link;
private String comments;
private String announcer;
private String replyTime;
|
其中的代码都是 JavaBean 的属性以及 getter、setter
如果其实现 Parcelable,则是这样的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
|
public class PostEntity implements Parcelable {
private String name;
private String category;
private String link;
private String comments;
private String announcer;
private String replyTime;
@Override
public int describeContents() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags) {
dest.writeString(this.name);
dest.writeString(this.category);
dest.writeString(this.link);
dest.writeString(this.comments);
dest.writeString(this.announcer);
dest.writeString(this.replyTime);
}
public PostEntity() {
}
protected PostEntity(Parcel in) {
this.name = in.readString();
this.category = in.readString();
this.link = in.readString();
this.comments = in.readString();
this.announcer = in.readString();
this.replyTime = in.readString();
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity>() {
public PostEntity createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new PostEntity(source);
}
public PostEntity[] newArray(int size) {
return new PostEntity[size];
}
};
|
在实现Parcelable的时候我们需要重写两个方法
public void writeToParcel(Parcel dest, int flags)public int describeContents()
其中describeContents只需要返回 0 即可
writeToParcel方法中我们把需要序列化的属性使用writeXXX的方式写入 Parcel 。
之后是 CREATOR 对象,这个对象负责从 Parcel 中读取对象,所以我们需要重写其方法来读取对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| protected PostEntity(Parcel in) {
this.name = in.readString();
this.category = in.readString();
this.link = in.readString();
this.comments = in.readString();
this.announcer = in.readString();
this.replyTime = in.readString();
}
public static final Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> CREATOR = new Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity>() {
public PostEntity createFromParcel(Parcel source) {
return new PostEntity(source);
}
public PostEntity[] newArray(int size) {
return new PostEntity[size];
}
};
|
这一段就是其实现方式,可见主要是将对象从 Parcel 中读取出来。
Kotlin实现
看过了冗长的 Java 实现方式,我们来看看kotlin是如何实现的吧。
首先使用插件将其转换为 Kotlin 文件,并修改其中的错误
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| class PostEntity : Parcelable {
var name: String? = null
var category: String? = null
var link: String? = null
var comments: String? = null
var announcer: String? = null
var replyTime: String? = null
override fun describeContents(): Int {
return 0
}
override fun writeToParcel(dest: Parcel, flags: Int) {
dest.writeString(this.name)
dest.writeString(this.category)
dest.writeString(this.link)
dest.writeString(this.comments)
dest.writeString(this.announcer)
dest.writeString(this.replyTime)
}
constructor() {
}
protected constructor(`in`: Parcel) {
this.name = `in`.readString()
this.category = `in`.readString()
this.link = `in`.readString()
this.comments = `in`.readString()
this.announcer = `in`.readString()
this.replyTime = `in`.readString()
}
companion object {
val CREATOR: Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> = object : Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> {
override fun createFromParcel(source: Parcel): PostEntity {
return PostEntity(source)
}
override fun newArray(size: Int): Array<PostEntity?> {
return arrayOfNulls(size)
}
}
}
}
|
这就是 Kotlin 实现 Parcelable 的方式了
优化
经过插件转化的 kotlin 代码其实使用的还是 java 的方式和 java 的思想,我们可以将其完全转化为 kotlin 的方式并对其优化
首先把其转化为数据类,这样会自动为我们生成
equals()/hashCode()toString()componentN()copy()
我们只需要将其改为这样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| data class PostEntity(var name: String? = null,
var category: String? = null,
var link: String? = null,
var comments: String? = null,
var announcer: String? = null,
var replyTime: String? = null
) : Parcelable {
override fun describeContents(): Int {
return 0
}
override fun writeToParcel(dest: Parcel, flags: Int) {
dest.writeString(this.name)
dest.writeString(this.category)
dest.writeString(this.link)
dest.writeString(this.comments)
dest.writeString(this.announcer)
dest.writeString(this.replyTime)
}
protected constructor(`in`: Parcel) : this() {
this.name = `in`.readString()
this.category = `in`.readString()
this.link = `in`.readString()
this.comments = `in`.readString()
this.announcer = `in`.readString()
this.replyTime = `in`.readString()
}
companion object {
val CREATOR: Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> = object : Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> {
override fun createFromParcel(source: Parcel): PostEntity {
return PostEntity(source)
}
override fun newArray(size: Int): Array<PostEntity?> {
return arrayOfNulls(size)
}
}
}
}
|
再之后观察发现,所有的 Parcelable 都需要有一个 CREATOR
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| companion object {
val CREATOR: Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> = object : Parcelable.Creator<PostEntity> {
override fun createFromParcel(source: Parcel): PostEntity {
return PostEntity(source)
}
override fun newArray(size: Int): Array<PostEntity?> {
return arrayOfNulls(size)
}
}
}
|
此处使用了 Kotlin 的伴生对象,使得调用 CREATOR 类似于 Java 中的静态属性
可以使用 Kotlin 的函数式编程特性抽取
新建文件ParcelableExt.kt
1
2
3
4
5
| public inline fun createParcel<reified T : Parcelable>(crossinline createFromParcel: (Parcel) -> T?): Parcelable.Creator<T> =
object : Parcelable.Creator<T> {
override fun createFromParcel(source: Parcel): T? = createFromParcel(source)
override fun newArray(size: Int): Array<out T?> = arrayOfNulls(size)
}
|
此处使用了 Kotlin 的内联函数,然后我们就可以将 PostEntity 精简为如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| data class PostEntity(var name: String? = null,
var category: String? = null,
var link: String? = null,
var comments: String? = null,
var announcer: String? = null,
var replyTime: String? = null
) : Parcelable {
override fun describeContents(): Int {
return 0
}
override fun writeToParcel(dest: Parcel, flags: Int) {
dest.writeString(this.name)
dest.writeString(this.category)
dest.writeString(this.link)
dest.writeString(this.comments)
dest.writeString(this.announcer)
dest.writeString(this.replyTime)
}
protected constructor(`in`: Parcel) : this() {
this.name = `in`.readString()
this.category = `in`.readString()
this.link = `in`.readString()
this.comments = `in`.readString()
this.announcer = `in`.readString()
this.replyTime = `in`.readString()
}
companion object {
val CREATOR = createParcel { PostEntity(it) }
}
}
|
总结
虽然可以直接将 Java 文件转化为 Kotlin 文件,但这样毕竟没有办法学习到 Kotlin 的精髓
使用一门语言就应该按照这门语言的编码风格以及规范去实现,这样才会让我们的学习更加有效率且养成良好的编码习惯
Kotlin 是一门典型的函数式编程语言,学习它的风格有利于我们了解函数式编程思想
在实现 Parceable 时我们使用了 Kotlin 的几个特性
查阅官方文档完成的同时我也学会了新的姿势知识,想一想也有点小激动呢